|
|
|
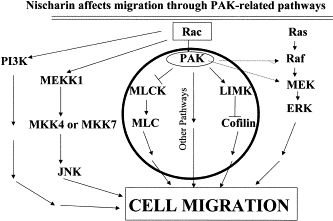
| The figure shows a proposed model for the role of Nischarin in Rac stimulated cell migration. Rac 1 can be activated by various external stimuli and activates several downstream pathways. Nischarin does not affect cell migration mediated through the JNK or ERK pathways. Nischarin retards migration through PAK mediated pathways (shown in a circle). |
Tumor cell migration and invasion are important factors in development of solid tumors and are essential for metastasis to various organs. Recently, it has been shown that PAK regulates motile and invasive phenotypes of breast cancer cells through reorganization of actin cytoskeleton. In addition PAK1 plays a role in breast morphogenesis and differentiation. It has been suggested there is a functional correlation between high grade breast tumors and enhanced PAK kinase activity, and thus PAK may have an important role in in vivo tumorigenesis. Since both PAK1 and PAK4 have been shown to strongly promote growth in soft agar, and since Nischarin binds to both of these kinases, it seems likely that Nischarin may affect anchorage independent growth as well as tumor growth in nude mice and thus Nischarin may be an important regulator of cancer progression.
A movie of nischarin is shown below. Immunofluorescence localization of nischarin in adherent cells viewed using confocal microscopy. It may take a few moments for the movie to load. You may need QuickTime Player to view the movie. If you do not have QuickTime Player, click here to download.
Thus we are investigating the role of Nischarin in breast tumor progression, and also we are in the process of identifying proteins that interact with Nischarin in breast cancer cells using proteomics as well as yeast two-hybrid approaches. A detailed understanding of the mechanistic basis of these events can significantly advance the development of new therapeutic approaches for cancer.
Publications
Prooncogenic factors miR-23b and miR-27b are regulated by Her2/Neu, EGF, and TNF-α in breast cancer. Jin L 1, Wessely O, Marcusson EG, Ivan C, Calin GA, Alahari SK. Cancer Res. 2013 May 1;73(9):2884-96. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-2162. Epub 2013 Jan 21.
Quantitative analysis of random migration of cells using time-lapse video microscopy. Jain P1, Worthylake RA, Alahari SK.J Vis Exp. 2012 May 13;(63):e3585. doi: 10.3791/3585. J Vis Exp. 2012 May 13;(63):e3585. doi: 10.3791/3585.
PDZK1 is a novel factor in breast cancer that is indirectly regulated by estrogen through IGF-1R and promotes estrogen-mediated growth. Kim H1, Abd Elmageed ZY, Ju J, Naura AS, Abdel-Mageed AB, Varughese S, Paul D, Alahari S, Catling A, Kim JG, Boulares AH. Mol Med. 2013 Aug 28;19:253-62. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2011.00001.
Integrin-binding protein nischarin interacts with tumor suppressor liver kinase B1 (LKB1) to regulate cell migration of breast epithelial cells. Jain P 1, Baranwal S, Dong S, Struckhoff AP, Worthylake RA, Alahari SK. .J Biol Chem. 2013 May 31;288(22):15495-509. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.418103. Epub 2013 Apr 9.
Rac and Rab GTPases dual effector Nischarin regulates vesicle maturation to facilitate survival of intracellular bacteria. Kuijl C 1, Pilli M, Alahari SK, Janssen H, Khoo PS, Ervin KE, Calero M, Jonnalagadda S, Scheller RH, Neefjes J, Junutula JR. EMBO J. 2013 Mar 6;32(5):713-27. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2013.10. Epub 2013 Feb 5.
Molecular Characterization of the Tumor-Suppressive Function of Nischarin in Breast Cancer. Somesh Baranwal, Yanfang Wang, Rajamani Rathinam, Jason Lee, Lianjin Jin, Robin McGoey, Yuliya Pylayeva, Filippo Giancotti, Gerard C. Blobe and Alahari SK. JNCI J Natl Cancer Inst (2011) doi: 10.1093/jnci/djr350 First published online: September 14, 2011
Role of Rho GTPases and their regulators in cancer progression.Rathinam R, Berrier A, Alahari SK. Front Biosci. 2011 Jun 1;17:2561-71.PMID:21622195 [PubMed - in process] Related citations
Rho GTPase Effector Functions in Tumor Cell Invasion and Metastasis.Baranwal S, Alahari SK.Curr Drug Targets. 2011 Jul 1;12(8):1194-201.PMID:21561416[PubMed - in process]Related citations
Integrin subunits alpha5 and alpha6 regulate cell cycle by modulating the chk1 and Rb/E2F pathways to affect breast cancer metastasis. Yanfang Wang, Sylvia Shenouda, Somesh Baranwal, Rajamani Rathinam, Prachi Jain, Lili Bao, Siddhartha Hazari, Srikanta Dash and Alahari SK. Molecular Cancer, 2011 (IN PRESS).
Breast cancer stem cells: A new challenge for breast cancer treatment Jain P, Alahari SK Frontiers in Bioscience 16, 1824-1832, (1 January, 2011)
Integrin mediated function of Rab GTPases in cancer progression Subramani D and Alahari SKMolecular Cancer 2010, 9:312 (9 December 2010
miRNA control of tumor cell invasion and metastasis.Baranwal S, Alahari SK. Int J Cancer. Oct 29.(2010)
Important role of integrins in the cancer biology.Rathinam R, Alahari SK.Cancer Metastasis Rev. Jan 30 .(2010)
Stromal cells and integrins: conforming to the needs of the tumor microenvironment.Alphonso A, Alahari SK.Neoplasia.Dec;11(12):1264-71. (2009)
MicroRNA function in cancer; Oncogene or a tumor suppressor. Shenouda, S.K. and Alahari S KCancer and Metastasis reviews. (In Press) (2009)
ST14 (suppression of tumorigenicity 14) gene is a target for miR-27b, and the inhibitory effect of ST14 on cell growth is independent of miR-27b regulation. Wang Y, Rathinam R, Walch A, Alahari SK. J Biol Chem. (2009)
Molecular mechanisms controlling E-cadherin expression in breast cancer (2009) Baranwal, S and Alahari, S.K.Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 384: 6-11
Ding Y, Milosavljevic T, Alahari SK. Nischarin inhibits LIM Kinase to regulate Cofilin phosphorylation and Cell Invasion. Mol Cell Biol. Mar 10 (2008)
Alahari, S.K., Reddig, P., Juliano, R.L. The integrin binding protein Nischarin regulates cell migration by inhibiting PAK. EMBO J, 23: 2777-2788 (2004)
Juliano, R.L., Reddig, P.J., Alahari, S.K., Edin, M.L., Howe, A.K., and Aplin, A.E., Integrin Regulation of Cell Signaling and Motility.Biochem., Society Transactions 32: 443-446 (2004)
Alahari, S.K. and H. Nasrallah : A Membrane proximal region of alpha-5 integrin is essential for its interaction with Nischarin. Biochemical Journal 15: 449-457 (2004)
Alahari, S.K.: Nischarin inhibits Rac induced migration and invasion of epithelial cells by affecting signaling cascades involving PAK. Exp. Cell Res. 288: 415-424 (2002)
Alahari, S.K., Reddig, P., Juliano, R.L. Biological aspects of signal transduction by cell adhesion receptors. Int. J. Cytology 220: 145-174 (2002)
Alahari, S.K.,: Mapping of the gene for Nischarin, a novel integrin binding protein, to chromosome 3 by fluorescence in situ hybridization). Intl. J. Human Genetics 1: 271-274 (2001)
Alahari, S.K., Lee, J.L., and Juliano, R.L.: NISCHARIN, a novel protein that interacts with integrin alpha-5 subunit, and inhibits cell migration. J. Cell Biology 151: 1141-1154 (2000)
Methods for study of integrin regulation of receptor tyrosine kinase and G protein coupled receptor signaling to MAP kinases. Methods In Enzymology 333:151-163 (2001)
Shock, D.D., Naik, U.P., Brittain, J.E., Alahari, S. K., Sondek, J., and Parise, L.V.: Calcium-dependent properties of CIB binding to the integrin alphaIIb cytoplasmic domain and translocation to the platelet cytoskeleton Biochemical Journal 342: 729-735 (1999)
DeLong, R.K., Hoon, Y., Alahari, S.K., Fisher, M., Short, S.M., Kole, R and Juliano, R. L.: Novel cationic amphiphiles as delivery reagents for antisense oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Research 27:3334-3341.(1999)
Hughes, J. A., Astriab,A., Yoo, H., Alahari, S.K., Liang, E., Sergueev, D., Shaw, B. and Juliano, R.L.: In Vitro Transport and delivery of oligonucleotides. Methods in Enzymology 313:343-359. (1999)
Juliano, R.L., Alahari, S.K., Yoo, H., Kole, R., and Cho, M. Antisense Pharmacodynamics: Critical issues in the transport & delivery of antisense oligonucleotides. Pharmaceutical Research 16: 494-502.(1999)
Alahari, S.K., Delong, R., Fisher, M.H., Dean, N. M. Viliet, P and Juliano, R.L. Novel chemically modified oligonucleotides provide potent inhibition of P-glycoprotein expression. J.Pharm.Exp. Therapeutics 286:419-428 (1998)
Howe.A., Aplin, A., Alahari, S.K., and Juliano, R.L.. Integrin signaling and cell growth Control.Current Opinion in Cell Biology 10: 220-231 (1998)
Aplin, A., Howe, A., Alahari, S. K., and Juliano, R.L. Signal transduction and signal modulation by cell adhesion receptors: the role of integrins, cadherins, IG-CAMS and selectins. Pharmacological Reviews 50: 197-263 (1998)
To search for all of Dr. Alahari's publications click here.
To return to Dr. Alahari's biography page click here.