Laboratory of Arthur L. Haas, PhDThe LSU School of Medicine and LSU Health Sciences Center are pleased to announce the establishment of the Arthur L. Haas Endowed Lectureship. An anonymous donor made a $100,000 gift to fund this lectureship in honor of Dr. Haas' illustrious career in research, mentoring, and academic leadership and to support higher education within the School's membership and the New Orleans public. read more...
Research Interests
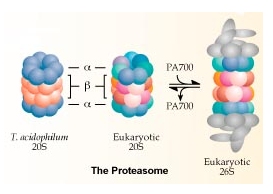
The end result of ubiquitination is degradation of the target protein by the 26S proteasome complex, a large (2MDa) multisubunit complex which recognises multi-ubiquitinated proteins and degrades them to small peptides. The ubiquitin chain is released and is broken up into single ubiqutin molecules which are then reused. The major role of ubiquitin conjugation is in targeting proteins for degradation as an essential regulatory step. Other roles for which conjugation has been implicated include gene regulation, DNA repair, stress response, cell cycle progression, various forms of muscle atrophy, and Alzheimers dementia. We have also identified a second constitutive system within cells that is parallel but distinct from ubiquitin in which the 15 kDa interferon-like protein ISG15/UCRP is conjugated to a smaller subset of intracellular targets. ISG15 is the archetype of a small group of function-specific ubiquitin-like proteins that includes SUMO-1 and Nedd8. The conjugation of ISG15 to intracellular targets functions to regulate protein-protein interactions, in one instance acting in trans to mediate association of the target with intermediate filaments. The general areas of work for both systems involve:
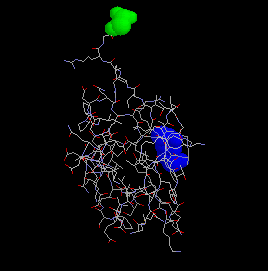
Ubiquitin is a small, 76 amino acid protein, which becomes covalently attached to other proteins via an isopeptide bond from Gly76 (green) of ubiquitin to the epsilon amino group of a lysine on the target protein. Ubiquitin Lysine48 is shown in blue.
If you are using a browser with the Chime plugin, click here to see a model of ubiquitin
that you can manipulate in 3D. |
|||
|
To search for all of Dr. Haas' publications click here.
|


 Ubiquitin is a highly conserved 8600 dalton polypeptide distributed throughout eukaryotes.
The biological effects of ubiquitin are exerted through a unique post-translational
modification in which the polypeptide is covalently ligated to free amino groups on
various intracellular target proteins in an ATP-coupled reaction.
Ubiquitin is a highly conserved 8600 dalton polypeptide distributed throughout eukaryotes.
The biological effects of ubiquitin are exerted through a unique post-translational
modification in which the polypeptide is covalently ligated to free amino groups on
various intracellular target proteins in an ATP-coupled reaction.